Spondylosis
March 15, 2024
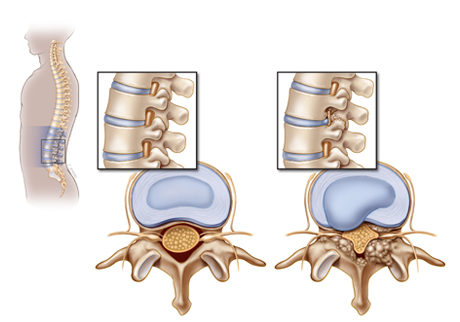
Cervical Spondylosis
March 15, 2024Physiotherapy Treatment for Frozen Shoulder
Frozen shoulder, also known as adhesive capsulitis, is a condition characterized by stiffness, pain, and limited range of motion in the shoulder joint. Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in managing symptoms and improving function for individuals with frozen shoulder. Here's a comprehensive treatment plan:
Causes of Frozen Shoulder:
The exact cause of frozen shoulder is not always clear, but several factors may contribute to its development:
- Immobilization: Prolonged immobilization of the shoulder joint due to injury, surgery, or medical conditions can lead to the development of adhesions and stiffness in the joint capsule.
- Inflammation: Inflammation of the shoulder joint, often associated with conditions such as arthritis or rotator cuff injury, can trigger the formation of scar tissue and adhesions, contributing to frozen shoulder.
- Age and Gender: Frozen shoulder tends to occur more frequently in individuals over the age of 40, and it is more common in women than men.
- Systemic Diseases: Certain systemic diseases such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, and cardiovascular disease may increase the risk of developing frozen shoulder.
Physiotherapy Treatment:
Pain Management:
- Modalities such as heat therapy, cold therapy, or ultrasound may be used to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation in the shoulder joint.
Range of Motion (ROM) Exercises:
- Passive and active-assisted range of motion exercises are performed to gradually restore flexibility and mobility in the shoulder joint.
Stretching Exercises:
- Gentle stretching exercises target the muscles and tissues surrounding the shoulder joint to improve flexibility and reduce stiffness.
Strengthening Exercises:
- Progressive strengthening exercises focus on improving the strength and stability of the shoulder muscles to support proper joint function and prevent recurrence of symptoms.
Joint Mobilizations:
- Manual therapy techniques such as joint mobilizations and manipulations may be used by the physiotherapist to gently mobilize the shoulder joint and improve its range of motion.
Postural Correction:
- Education on proper posture and ergonomic principles helps minimize strain on the shoulder joint and promote optimal alignment during daily activities.
Functional Training:
- Functional exercises and activities are incorporated to simulate real-life movements and improve the patient's ability to perform daily tasks with ease.
Patient Education:
- Providing education on the condition, its causes, and self-management strategies empowers the patient to take an active role in their recovery and prevent further complications.