Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
March 16, 2024
Ankle Sprain
March 16, 2024Physiotherapy Treatment for Osteoarthritis
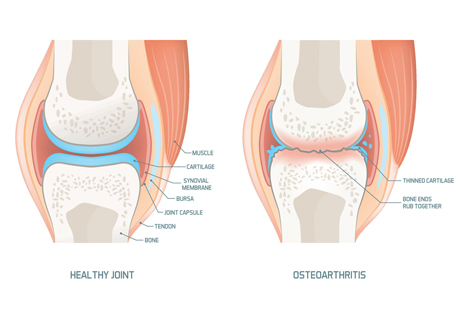
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage in the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in managing symptoms, improving function, and enhancing quality of life for individuals with osteoarthritis. Here's a comprehensive treatment plan:
Causes of Osteoarthritis:
Several factors may contribute to the development of osteoarthritis:
- Age: Osteoarthritis is more common in older adults, as the wear and tear on joints over time can lead to the breakdown of cartilage and joint degeneration.
- Joint Injury or Trauma: Previous joint injuries or trauma, such as fractures or ligament tears, can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis in the affected joint.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts added stress on weight-bearing joints, such as the knees and hips, increasing the likelihood of developing osteoarthritis in these joints.
- Genetics: Genetic factors may predispose individuals to develop osteoarthritis, as certain genes can influence cartilage structure and joint health.
- Joint Misalignment: Structural abnormalities or joint misalignment can lead to uneven distribution of forces within the joint, contributing to cartilage degeneration and osteoarthritis.
Physiotherapy Treatment:
Pain Management:
- Modalities such as heat therapy, cold therapy, or transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) may be used to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation in the affected joints.
Exercise Therapy:
- Low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, or cycling help improve joint flexibility, strengthen supporting muscles, and reduce pain associated with osteoarthritis.
Joint Protection Techniques:
- Education on joint protection techniques, such as proper body mechanics and ergonomic principles, helps minimize stress on affected joints during daily activities.
Manual Therapy:
- Manual therapy techniques such as joint mobilizations, soft tissue massage, and stretching exercises help improve joint mobility, reduce stiffness, and alleviate pain.
Strength Training:
- Progressive strengthening exercises target the muscles surrounding the affected joints to improve stability, support proper joint alignment, and reduce joint stress.
Balance and Proprioception Training:
- Balance and proprioception exercises help improve joint stability and reduce the risk of falls, which is particularly important for individuals with osteoarthritis affecting weight-bearing joints.
Assistive Devices:
- Prescription and fitting of assistive devices such as orthotics, braces, or walking aids may be recommended to provide support and relieve pressure on affected joints.