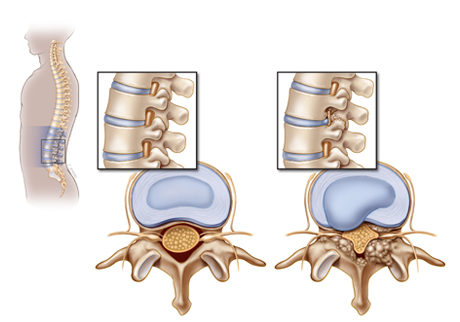
Osteoarthritis
March 16, 2024
Finger Fracture
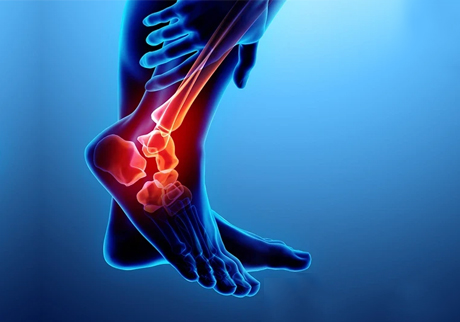
March 16, 2024Physiotherapy Treatment for Ankle Sprain
An ankle sprain occurs when the ligaments surrounding the ankle joint are stretched or torn, typically due to sudden twisting or rolling of the ankle. Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation process, helping to reduce pain, swelling, and instability, and promoting optimal healing and return to function. Here's a comprehensive treatment plan:
Causes of Ankle Sprain:
Several factors may contribute to the development of an ankle sprain:
- Traumatic Injury: Ankle sprains often occur as a result of sudden trauma or injury, such as landing awkwardly from a jump, stepping on an uneven surface, or twisting the ankle during physical activity.
- Ligament Weakness or Instability: Individuals with weak or lax ligaments may be more prone to ankle sprains, as the ligaments are less able to support and stabilize the ankle joint during movement.
- Poor Footwear: Inadequate footwear, such as shoes with insufficient support or traction, can increase the risk of ankle sprains by compromising the stability of the foot and ankle during activity.
- Muscle Weakness or Imbalance: Weakness or imbalance in the muscles surrounding the ankle joint, particularly the muscles of the lower leg and foot, can contribute to instability and susceptibility to injury.
Physiotherapy Treatment:
R.I.C.E. Protocol:
- Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation (R.I.C.E.) are initial measures to reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation in the acute phase of an ankle sprain.
Range of Motion Exercises:
- Gentle range of motion exercises help restore mobility in the ankle joint and prevent stiffness. Exercises may include ankle circles, ankle pumps, and toe taps.
Strengthening Exercises:
- Progressive strengthening exercises target the muscles of the ankle, lower leg, and foot to improve stability and support the injured ligaments. Exercises may include calf raises, ankle dorsiflexion/plantarflexion, and toe curls.
Balance and Proprioception Training:
- Balance and proprioception exercises help improve joint proprioception and neuromuscular control, reducing the risk of recurrent ankle sprains. Exercises may include single-leg balance, wobble board exercises, and agility drills.
Manual Therapy:
- Manual therapy techniques such as soft tissue massage, joint mobilizations, and proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) stretching may be used to reduce muscle tension, improve joint mobility, and promote healing.
Functional Rehabilitation:
- Functional rehabilitation involves specific exercises and activities that mimic daily or sports-related movements to restore functional capacity and prepare the individual for a safe return to activity or sport.