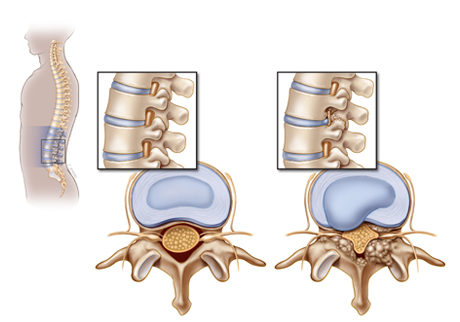
Cervical Spondylosis
March 15, 2024
Osteoarthritis
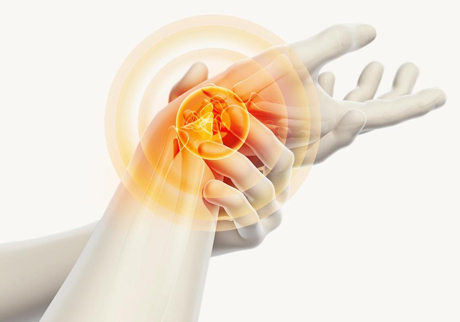
March 16, 2024Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome:
Several factors may contribute to the development of carpal tunnel syndrome:
-
Repetitive Movements: Activities or occupations that involve repetitive hand and wrist movements, such as typing, assembly line work, or playing musical instruments, can increase the risk of developing CTS.
-
Hand and Wrist Positioning: Prolonged or awkward positioning of the hand and wrist, especially during activities that involve bending or flexing the wrist, can lead to compression of the median nerve.
-
Trauma or Injury: Trauma to the wrist, such as fractures or sprains, can cause swelling and inflammation within the carpal tunnel, putting pressure on the median nerve.
-
Underlying Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, thyroid disorders, and pregnancy, may predispose individuals to develop CTS.
Physiotherapy Treatment:
Pain Management:
- Modalities such as ultrasound, cold therapy, or electrical stimulation may be used to reduce pain and inflammation in the wrist and hand.
Splinting:
- Wrist splinting is often prescribed to immobilize the wrist in a neutral position and relieve pressure on the median nerve, especially during periods of rest or sleep.
Stretching Exercises:
- Gentle stretching exercises target the muscles and tendons surrounding the wrist and forearm to alleviate tightness and improve flexibility.
Strengthening Exercises:
- Strengthening exercises focus on improving the strength and endurance of the muscles in the hand, wrist, and forearm to support proper joint alignment and reduce strain on the median nerve.
Nerve Gliding Techniques:
- Nerve gliding or flossing exercises help mobilize the median nerve and reduce adhesions within the carpal tunnel, promoting optimal nerve function and reducing symptoms.
Ergonomic Modifications:
- Education on proper ergonomics and workstation setup helps minimize repetitive strain on the wrist and hand during daily activities, reducing the risk of exacerbating CTS symptoms.
Activity Modification:
- Encourage modifications to activities or work tasks that exacerbate symptoms, such as taking frequent breaks, alternating tasks, or using ergonomic tools and aids.